Article
How Enterprise Systems Benefit Your Business

At a high level, enterprise systems automate workflows and processes. Under the hood, they’re large-scale software packages that track and control business operations. For users, they provide a centralized command hub for essential business operations.
Enterprise systems are usually technological ecosystems that incorporate a variety of applications, protocols, and formats. To create them, developers have to be versatile.
At Fresh, our emphasis on security, scalability, and efficiency define our approach. But we also emphasize consultative expertise. This approach equips us to create enterprise systems for businesses across industry verticals: layered software that demystifies complexity, solves problems, and makes operations more effective.
Let’s dive into an overview of effective enterprise system creation.
How Enterprise Development is Unique
In smaller-scale traditional web app development, there’s less abstraction. For enterprise systems, developers need to understand an interconnected technological ecosystem. They must also understand the various workflows and processes the software will automate.
Suffice it to say, strategy and planning are essential. Upfront, you’ll need to consider the system’s scalability and future growth. Because the ERP system will grow and mature, creating a reusable code base is vital to saving time and money.
One notable differentiator at Fresh is our emphasis on usability. Enterprise systems are complex, but operation and maintenance don’t have to be. We keep that principle at top of mind when designing for clients: build the right product, and build the product right. Enterprise software satisfies requirements and becomes usable for those without technical expertise.
How Enterprise Systems Have Changed and Where They are Going
In recent years, containerization and deployment automation have been the main factors contributing to the evolution of enterprise systems. Here’s how enterprise systems contribute to business functions:
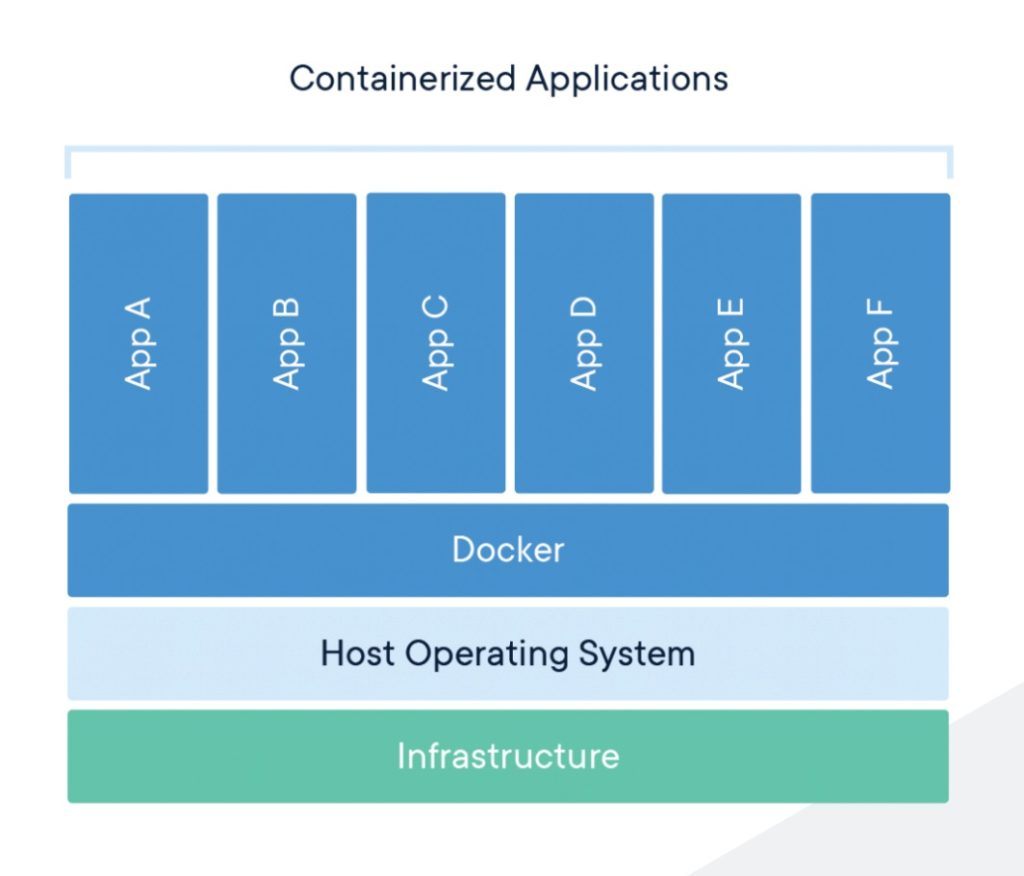
Containerization (Using Docker)
Containers “package up code and all its dependencies.” According to Docker, they allow applications to “run quickly and reliably from one computing environment to another.” Docker virtualizes application elements in one unified infrastructure.
This approach makes it more scalable and less expensive. Streamlined development environments and automated dev workflows save time and resources while also allowing teams to focus on things like software roadmaps and design.
(Image Source: Docker)
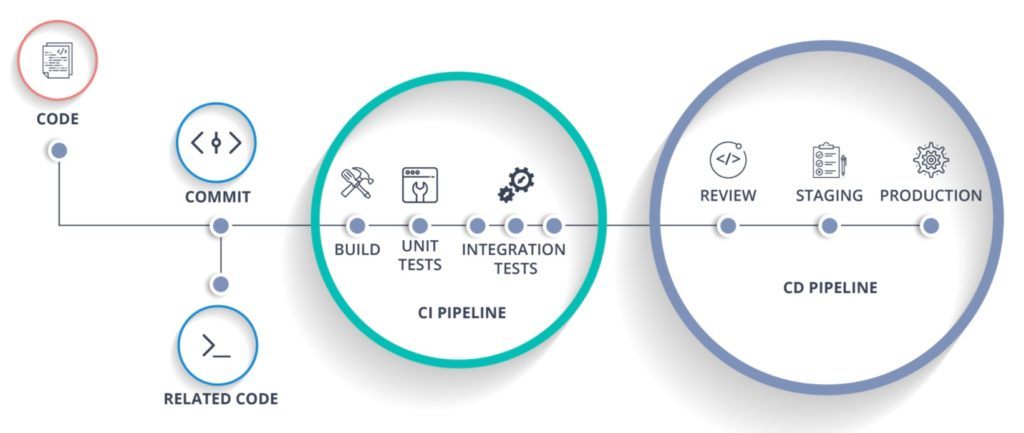
Automation
A CI/CD pipeline (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) “bridges the gap between development and operations teams.” It allows for the process of assembly and testing to be automated. In effect, CI/CD pipelines standardize and automate the delivery process for applications.
With automation, rapid, scalable development is possible for a wider range of companies.
(Image Source: DZone)
What Are the Different Types of Enterprise Systems?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Enterprise resource planning software collects and organizes business information technology, data, and resources. ERP enables companies to improve their business’ organization and allocation of resources. Examples include digitizing traditionally manual processes like production, sales quoting, and operations.
A company can use an ERP to manage and streamline operations. This allows people to do work that an automated system can’t.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Relationship Management systems support your company’s interactions and relationships with customers. With customer data and information stored in one place, sales communication, customer service, and relationship management are more effective.
Consider the following example: A potential high-value customer drops out of the sales conversion funnel at a crucial step. A CRM can flag the interaction, and the sales team can use the data to address future issues.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SCM software controls the information flows of goods and services. From acquiring raw components to distributing the product to the consumer, SCMs are on point. Bottlenecks are inherent to logistical computing systems, and SCMs provide unprecedented levels of control and predictability.
What Benefits Can You Expect from an Enterprise System?
The core value of enterprise systems is that they support legacy business processes. They make operations more efficient by centralizing and standardizing access to all company systems.
When working in a large company, sharing information is often decentralized. Data is distributed among individual legacy systems, with specific functions and regions. Companies start with one service and expand, which makes the above true for almost any mature organization.
Whatever the industry, a unified flow of data in the upstream and downstream of a company is essential.
Enterprise systems provide immediate insights into real-time data to simplify complex workflows which will result in increased transparency, higher productivity, and greater corporate momentum.