Article
An Introduction to Industrial Design Terminology
Industrial design is a creative discipline focused on solving real-world problems with a blend of art and design, technology, and science.
Like other fields influenced by the philosophy of human-centered design, industrial design drives innovation through a combination of practical ideas and scientific processes. The end result is physical products that delivers on business goals, being both user-friendly and feasibly manufacturable.
The industrial design community is passionate – 50 plus definitions exist on the Industrial Designers Society of America website that you can explore in the link.
The Relationship Between Products and People
At top of mind for industrial designers are three questions:
- How will the product be used?
- How it will affect its users?
- How can I create an efficient relationship between a user and the product?
Rather than focusing solely on aesthetics or mechanics, industrial designers use each of these to improve a product’s value.
And as with any discipline, industrial design carries its own unique set of terms that designers use to more effectively communicate with one another. Similarly, the terms can be used on the business facing side to communicate with the designers doing the creative work.
In either case, the goal is developing a shared vocabulary when answering the aforementioned questions, leading to more efficiency during product development and a better end product.
Terms Clients Should Know
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a list that contains quantities of every component and raw material required to create a specified assembly. It serves as the first step and foundation for any industrial design project.
A “Cost BOM” includes pricing information, while an “Indented BOM” displays all the parts needed for an assembly in a parent-child & top-down method.
Both of these examples of BOMs are important for stakeholders and designers alike, ensuring that all parties are on the same page as the product is designed.
As a client, you should also be aware of different types of manufacturers, distinguished below:
Original Design Manufacturer (ODM): A company that designs and manufactures products for other companies to sell as their own. Sometimes the design is first created by the ODM and sold to a brand, and other times the brand provides its own design specification.
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM): A company that manufactures components and/or finished products for other companies. Many brands use OEMs to complete some or all of their manufacturing.
General Terminology
Below is a list of general terminology (which will be expanded upon in future posts) that give a sense for what industrial design entails and how the discipline is executed.
Assembly: Assembly is both a noun and a verb – the process of creating something, and the end product of an assembly process. An assembly is usually made up of multiple parts. It can be a physical object or a digital model of a 3D object created in software such as SOLIDWORKS.
Casting: A manufacturing process where molten metal is poured into a mold. Casting pertains to anything from precision machinery and electrical hardware to decorative hardware and electric motors.
Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC): Programmed or automated machinery that is controlled via computer and used to produce accurate prototypes, tools, and components. Laser cutters, mills, and grinders can all be CNC machinery.
Die: A tool (made from a metal block) used to cut or shape manufacturing material.
Mold: A form used to create similarly-shaped plastic or metal forms, typically through mass production. Molds are usually made of metal and can work via injection molding or casting.
Off-Tool Sample (OTS): A sample used to make sure that the manufacturing process is creating desired results, the assembly works as it should, and the manufacturing process is free of problems. An OTS is used to check whether production tooling is tuned correctly and fix any flaws in the design prior to making production quantities. There are often at least two OTS versions created during a project.
Part: Similar to a component, a part is exactly what you’d imagine – a single piece of an assembly. But a part can be a digital or physical representation of a piece. A digital example would be a part file in software such as SOLIDWORKS.
Scale: A way to create smaller or larger versions of an object while maintaining proportions, usually used when an object is too large or small to practically demonstrate otherwise. For example, a designer might show a desk at 1:7 scale (one-seventh of full size) so that it fits on a piece of paper.
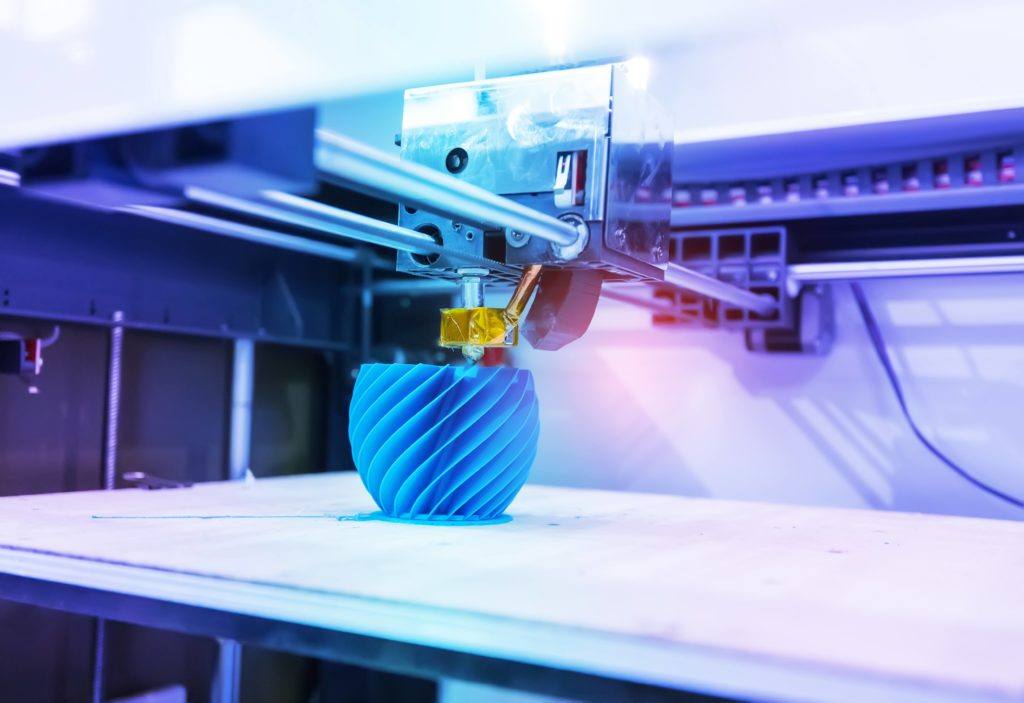

Terms Related to 2D and 3D Renderings
A Control Drawing, also called an engineering drawing or technical drawing, is a collection of 2D renderings of a finished assembly. It includes information like measurements, tolerances, and other notes that cannot be obtained from a 3D rendering alone.
3D Printing: These are processes for making 3D objects, usually done by adding thin slices of material onto one another until a finished object is created. Common 3D printing processes include FDM (fused deposition modeling), SLA (stereolithography), SLS (selective laser sintering), and more.
Lastly, if you’re familiar with other sub-disciplines of design, file types can get confusing. With respect to 3D Printing, you should be aware of:
3D File Types (Common): 3DS, ASM, DAE, FBX, IGES, OBJ, PLY, PRT, STEP, STL, WRL, X_T.

Awards
Industrial designers take pride in their work, and as with most design disciplines, there are a variety of ID awards. Below are a few that you can look for when choosing a vendor.
Awards Related to Industrial Design:
Red Dot Award: An international award given to businesses that have distinguished themselves through industrial design. It is awarded for excellence in product design, communication design, and other design concepts.
International Design Excellence (IDEA) Award: An industrial design award given to brands that help develop public awareness and passion for industrial design. The award is presented by the Industrial Design Society of America (IDSA).
Good Design Award: One of the longest-running and most prestigious awards given in industrial design. It’s awarded to companies that push the envelope and raise the bar in the world of design.
iF Product Design Award: An international award given for innovation and excellence in product design.