Article
Which Companies Are Propelling the AI Movement?

Whether you realize it or not, whenever you browse the internet, listen to music, drive your car, or use your phone, AI is involved.
In 2017, there were already four billion AI-powered devices in use worldwide. Some of the biggest tech companies in the world, including Apple, Uber, Facebook, and Microsoft, have dedicated significant resources to AI and are using it to improve their products. AI gives businesses the ability to meet consumer demands more effectively, both directly (such as with personal assistants) and indirectly (such as by using AI to make smarter suggestions to consumers).
What Are the Biggest Names in AI Working On?
Amazon
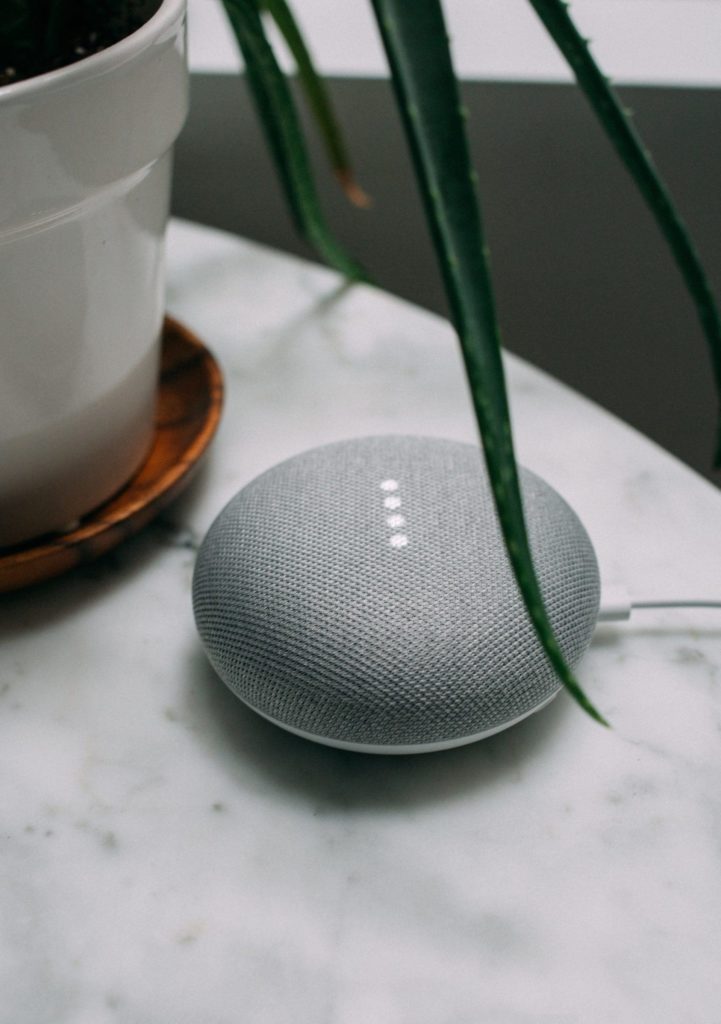
Amazon has been working on its line of Echo products for the past several years. These are their signature smart speakers that use an AI assistant, Alexa, to help users with common tasks and routines, like streaming music and video, checking the weather, setting reminders, searching the internet, and more.
The first version of the Echo was released to the public in 2015 and has become one of the most popular home personal assistants. Since the first Echo product was announced, various versions have been released with different sizes and capabilities. Amazon has also partnered with individuals like Peter Thiel and Elon Musk to begin monitoring AI development and promoting responsible practices in the industry.
Google is leading the charge on AI development. The tech behemoth has been working on implementing AI in all of its services, from the Assistant embedded in Android phones to the way we search for things on Google, watch videos on YouTube, access our photos in Google Photos, and even how Android phones take pictures. Pixel 3, a smartphone developed and released by Google, was reviewed as having the best smartphone-class camera in the market at the time of its release. Despite having less hardware than competing devices, Google managed to achieve impeccable image quality strictly through AI processing.
The company is pursuing the technology at a breakneck pace, having purchased several AI startup companies in the last few years, and is making massive strides in the area. The most significant of these purchases have been DeepMind, a British AI research company discussed further down this list.
Apple
Apple was the first company to debut a virtual assistant with the iPhone 4s. It’s important to note that the Siri AI was an acquisition by Apple in 2010 when it purchased Siri, Inc. At that time, Apple made the decision to remove features from Siri, believing that the advanced AI may actually confuse and scare customers. While Siri dominated the smart assistant market for a while, she was passed by Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa in several areas of functionality.
Apple also uses machine learning in other areas of their ecosystem. For instance, the cameras on iPhones use neural networks to not only take better photos but perform tasks in real time that used to only be possible with a traditional camera. At the release of the iPhone X they announced that machine learning would be incorporated in all of their new phones. While its function is still mostly underneath the surface, many of the new iPhone features, like FaceID, use AI. We will likely see more examples of this as time goes on.
AIBrain
AIBrain is an artificial reality development company whose goal is to create AI software that will eventually become fully autonomous, and they are funding this ambition by providing consumer electronics companies with AI solutions. AIBrain is working on projects in various areas like robotics, customer service, game development, and the service industry.
One example of this is their product Athena, an autonomous virtual assistant that can navigate and learn from its surroundings to assist customers. It does this via SLAM technology, which allows the assistant to build a map of its surroundings and determine its location without any prior knowledge of its whereabouts. Their other products are Tyche (an AI for young child development), Smile (an AI to help children learn social and emotional skills), Futurable (a game that simulates aspects of the real world with the intention of teaching AI how our world works), and dAIsy (a virtual assistant for learning new languages)
Facebook is taking an open-source approach to AI. Rather than creating their AI tech behind closed doors, they have released several of their frameworks and software for creating AI systems, giving indie developers the tools and resources to begin working on AI themselves. They have four AI labs around the world, all working on different aspects of AI. While some of these are for the company’s social media site (like an AI Assistant for their Messenger platform), they are also working towards the general advancement of AI technology.
In 2016, Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg also introduced an AI he built for his home called JARVIS, which he named after the AI from Iron Man. JARVIS gives us an idea of what living with a more sophisticated assistant could look like and shows that the technology might not be as far off as we think.
Deepmind
DeepMind, an AI startup company owned by Google, is primarily concerned with research. While they do offer to sell their software to companies open to their mission, they do not produce any actual products. Instead, they use their funding from Google and other supporters to advance AI, creating formal research papers on the subject about the practical applications of AI.
Their main area of focus is the impact AI will have on the healthcare industry and our society at large. DeepMind’s Ethics and Society department is working to predict how fully autonomous AI will affect the various aspects of our day-to-day lives, our industries, and how we can manage it responsibly and safely, and, of course, they are also contributing their research directly to Google’s own products, helping them develop smarter assistants and more energy-efficient practices.
IBM
IBM, one of the most influential tech companies of the last century, has been working on an AI called Watson for the past several years. While Watson first gained notoriety for beating the Jeopardy! world champion, IBM has continued to develop the program for business applications.
What sets Watson apart from other AI is its ability to perform the same tasks as other AI entities with less information. By “training” Watson, businesses can use the software to make more informed decisions, share the knowledge and experience of each employee with all employees, predict and prepare for disruptions, and detect liabilities. Watson also keeps an employer’s data completely secure; it is a self-contained system designed to protect a company and improve its effectiveness.
Microsoft
Microsoft’s approach to the artificial intelligence field has centered around helping developers understand and utilize AI concepts, working with companies to create new workflows, and demystifying this technology through research and easily accessible explanations of the inner workings of AI programs.
Their Azure cloud service now includes AI software that can be used by developers and enterprises to make AI development faster and simpler. Azure’s Cognitive Service gives users access to over 24 cloud-based APIs for various aspects of AI, including vision, speech, knowledge, search, and language. These APIs make it faster and simpler to begin employing AI, as well as offer the security and privacy that comes with Microsoft systems.
Wrap Up
It’s not just these big companies that are making waves in AI; countless smaller companies are working on crucial projects to move AI forward. To read more about them, check out our blog post: The Progression of AI: A Technology for Enhancing Productivity.